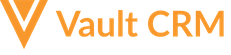Customizing Email Header Behavior
Each email template can be configured to have a unique from, reply-to, and sending domain header. You may want specific emails to be from the user (User.Email), and others from a fixed email address, for example always from brand@customer.com. For details on how these values are set by Approved Email Content Admins, see Creating a Sending Domain.
Who can use this feature?
- Content Admin Users — Browser
- Using Customized Email Header Behavior
- Users require an Approved Email license
Configuring Customized Email Header Behavior for
To configure this feature, ensure Configuring Approved Email is complete.
Using Customized Email Header Behavior as
Email headers are defined by internet standards, and Veeva complies with these and email authentication standards, for example SPF, DKIM, DomainKeys, and SenderID.
- Define or modify the following email header values:
- From Address – this is the email address that displays in the From field in all email clients. This is a required field and is set on the Email Template document type.
- Subject – this is the subject that displays in all email clients. This is required.
- Sending Email Domain – This is the authenticated domain that emails are sent from and is set by the email engine in the <return-path>email header. This is required and can be configured in two ways:
- Sending Email Domain field on approved_document__v. This is optional and is set on the Email Template. When set in Vault, this value overrides the value set in the Approved Email Setting Approved Email Domain (approved_email_domain__v). This allows a product branded email template to be sent from a brand.com authenticated domain. When this setting is null, the default value is used (see below).
- Approved Email Setting Approved Email Domain (approved_email_domain__v). This is the default when a value is not set on the Email Template. A unique domain can optionally be defined for each user Profile. The common example is for multi-country orgs where the sending domain is different for each country.
- From Name – this is the descriptive name (for example, first name and last name) that email clients display. This is optional.
- Reply To Address – this is the email address that replies are sent to. This can be different from the From Address. (If not set, replies go to the From Address.) This is optional.
- Reply To Name – this is the descriptive name that email clients display. This is optional.
- Verify the sending domain is the same as the domains used in the from address header. In general, these domains should be the same. For example, if the from address is user@company1.com, configure the sending domain as company1.com. This offers two advantages:
- Email clients do not display a message that indicates a mismatch between these domains. For example, Outlook typically displays this message in the format From user@company1.com on behalf of company2.com. Gmail typically displays it as From user@company1.com via company2.com.
- Slightly higher ability to deliver email directly to the recipient’s inbox
- To verify your email domain is set up correctly, use Port25. To receive the results in your email address, the address needs to be added to the check-auth address.
For example, to send the results to: jsmith@yourdomain.com, the sample message should be sent to check-auth-jsmith=yourdomain.com@verifier.port25.com.
A reply email is sent back to you with an analysis of the messages authentication status. The report performs the following checks: SPF, SenderID, DomainKeys, DKIM and Spamassassin.
The following are examples of how the From and Reply-to headers can be configured on Email Templates in Vault. For reference, User.Email uses the email address from the User record, and User.Name uses the end user's name. This assumes the user’s name is Employee One, and her email address is employeeone@company.com.
Example 1
|
|
From Address |
From Name |
Reply-to Address |
Reply-to Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example Values |
{{userEmailAddress}} |
{{userName}} |
n/a |
n/a |
Displays as from: Employee One <employeeone@company.com>
Replies go to: Employee One <employeeone@company.com>
Example 2
|
From Address |
From Name |
Reply-to Address |
Reply-to Name |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example Values |
{{userEmailAddress}} |
{{userName}} |
replies@brand.com |
Customer Service |
Displays as from: Employee One <employeeone@company.com>
Replies go to: Customer Service <replies@brand.com>
Example 3
|
|
From Address |
From Name |
Reply-to Address |
Reply-to Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example Values |
name@company.com |
{{userName}} |
n/a |
n/a |
Displays as from: Employee One <name@company.com>
Replies go to: Employee One <name@company.com>