Adding Data to X-Pages in X-Pages Studio
Content creators can add and filter data for X-Pages using data elements. After adding and previewing the data, content creators can define the layout. See Defining X-Pages Layouts for more information.
When content creators edit an existing Data Element and add or remove a field, all data elements using that Data Element as the source are updated to include the new field or remove the field. This applies even if there are multiple Data Elements created on top of each other - the new field is populated in each or removed in each.
Who can use this feature?
- Content Creators - Browser
- Adding Data Elements
- Using Get Data Elements
- Using Calculate Data Elements
- Users do not require an additional license
Configuring Data Elements in X-Pages Studio for
To configure this feature, ensure Configuring X-Pages Studio is complete.
Optional Configuration
To configure the Get Nitro data element:
- Ensure the X-Pages Studio test user has access to Nitro.
- Ensure Nitro is configured to share data with Vault CRM. See Configuring Nitro Data Sync for Vault CRM X-Pages.
Adding Data Elements as
To add a data element to a page:
- Select the page name or select Edit from the Actions menu for the page you want to add a data element to. The Data Palette page displays.
- Select Add Data Element.
-
Select the Element Type.
-
Select Next.
- Populate the Name field.
-
Enter the appropriate information for the data element.
- Select OK.
- Select the Refresh button in the Preview section to view the resulting data. Preview the data often to ensure the results are reasonable.
-
Select Save once all of the desired data elements are added. If there are no errors in the content, a deployable version of the content is created.
Defining Where Clauses for Query Data Elements
When defining Where clauses for a query data element to filter the data results, users must include a field on the queried object, an operator, and an expression. The expression can use data from other data elements. The operators available for selection in a Where clause depend on the data type of the selected field.
|
Field Data Type |
Compatible Operators |
|---|---|
|
Any (String, Number, Date, Bool) |
|
|
Comparable (String, Number, Date) |
|
|
String |
In |
Vault Field Types
The following field types are supported:
Considerations for Creating Queries
To ensure cross-platform functionality for X-Pages once they are deployed, consider the following when creating queries:
- IDs and field values must be surrounded with single quotes if the query can be used on Browser. Otherwise, the query fails.
- Queries referencing object names, field names, IDs, and field values must match exactly if the query can be used on Browser or mobile devices. For example, a query on Calls that filters data using the Channel type picklist value Face_to_face_vod must use Face_to_face_vod in the query. Otherwise, the query might fail.
Using Get Data Elements as
When content creators edit an existing Data Element and add or remove a field, all data elements using that Data Element as the source are updated to include the new field or remove the field. This applies even if there are multiple Data Elements created on top of each other - the new field is populated in each or removed in each.
The following get data elements are available:
- Context Data - query a field value from the vault based on the current user
- CRM Data - query data records from the vault
- Aligned Territories - return a list of aligned territories for the current user
- Data Box (formerly CRM Data Engine) - return large data sets from Data Box
- Nitro Data - query data from Nitro based on the current user
- Translated Field Names - get the singular and plural translations of object field names
- Translated Object Names - get the singular and plural translations of an object name
- Messages - query Veeva Messages from Vault CRM
- Current Date - get the current date as a single record with a single value
- Current Datetime - get the current date and time as a single record with a single value
- Territory Feedback - query data for territory feedback
Using Context Data
Users can query a field value from the vault based on the current user using Context Data. The objects available depend on the selected object type.
|
Object Type |
Context Query Objects |
|---|---|
|
|
| account_plan__v |
|
|
call__v |
|
|
|
| inventory_monitoring__v |
|
|
opportunity_management__v |
user__v |
| orders__v |
|
|
patient_center__v |
user__sys |
|
service_center__v |
user__sys |
|
territory_feedback__v |
user__sys |
|
user__sys |
Users can populate the following information when creating a query:
- Object – A CRM object available for the selected page type for which the user has at least Read access
- Field – A field on the object to display. Only fields for which the user has read permission are available.
A context query returns a single record with a single field as output.
Using CRM Data
Users can query data records from Vault CRM using Vault CRM Data. The Vault CRM Data query can return a single record or a list of records as output, depending on the limit defined by the user. Each record can contain one or more fields.
Users can specify the following parameters when creating a query:
- Object – Any Vault object for which the user has at least Read access
- Fields – Fields on the object to display. Only fields for which the user has read permission are available. Multiple fields can be selected.
- Object Type Field - Object type of the selected object. The object type ID, API name, and translated label are returned. When previewed, the translated value respects the language setting of the selected test user. If a translation for the test user's language is not available, English is used.
Querying the Object Type directly is not supported using Vault CRM Data. If you open migrated content containing a query against the Object Type, an error message displays. Utilize the Object Type Field translation functionality to find API or Translated values.
- Limit (optional) – Number of records to display. Preview displays a maximum of 200 records regardless of the limit set.
- Sort (optional) – Display order of the records based on field values
- Where Clause (optional) – List of individual or grouped WHERE clauses joined by AND or OR. See Defining Where Clauses for more information.
Strings defined in the where clause are case sensitive in content deployed to iPad.
Using Aligned Territories
Users can view a list of aligned territories for the current user using Aligned Territories. Content creators can select to include the child territories for each aligned territory.
Using Data Box (formerly CRM Data Engine)
When content creators add Data Box to an X-Page, users can view large data sets queried from Data Box. Data for this element is obtained by running the queryDataEngine method. Users can preview the results from this query in the X-Pages Studio preview.
Users must populate the following information:
- Data Table - Tables available for the current user, as returned by getDataEngineTables
- Fields - Field options compatible with the queryDataEngine JS method, both dimensions and metrics
The following fields are optional:
- Where - available operators:
- Equals
- Not Equals
- Greater Than
- Greater Than or Equal
- Less Than
- Less Than or Equal
- Between
- In
- Is Null
- Is Not Null
- Sort - Each sort key is composed of an available sort field from the selected object and a direction (Ascending or Descending). Available sort fields depend on whether the Fields input has any Metrics in it.
- Limit - If the limit is exactly 1, this is a Singleton data element; otherwise, this is a List of Records data element
Using Translated Field Names
Users can get the singular and plural translations of object field names using Translated Field Names. These values can be used as labels and values in data and display elements. When the X-Page is deployed to users in a multi-country vault, the labels are automatically translated in the correct language for each user. Users must populate the following information:
- Object – Any Vault object for which the user has at least Read access
- Fields – Any fields for which the user has read permission. Multiple fields can be selected.
Using Translated Object Names
Users can get the singular and plural translations of an object name using Translated Object Names. These values can be used as labels and values in data and display elements. When the X-Page is deployed to users in a multi-country vault , the labels are automatically translated in the correct language for each user. Users can select any Vault object for which they have at least Read access.
Using Messages
Users can query Veeva Messages from Vault CRM using Messages. This element queries existing Veeva Messages, so users must create any custom Veeva Messages in their vaults before they can be used in X-Pages Studio. Users can use custom Veeva Messages as translations for custom text, for example, using a field calculated by a One for One element as a label. When the X-Page is deployed to users in a multi-country Vault, the Veeva Message in the correct language displays for each user.
Users can select Add to query multiple Veeva Messages at once. Users must populate the following information for each Veeva Message:
- Category – Category of the Veeva Message
- Name – Name of the Veeva Message
Using Get Nitro
The Get Nitro element returns a single record or a list of records as the output, depending on the limit defined when the query was created. Each record can contain one or more fields.
Select or enter the following data element information:
- Table – Any Nitro table for which the test user has Read permission
- Fields – Fields within the selected table for which the test user has Read permission. Multiple fields can be selected.
- Limit (optional) – Number of records to display. Preview displays a maximum of 200 records regardless of the limit entered.
- Sort (optional) – Display order of the records based on field values
- Where Clause (optional) – List of individual or grouped WHERE clauses joined by AND or OR. See Defining Where Clauses for Query Data Elements for more information.
Using Current Date
Users can get the current date as a single record with a single value using Current Date. Users do not need to populate any additional information to retrieve this value.
Using Current Datetime
Users can get the current date and time as a single record with a single value using Current Datetime. Users do not need to populate any additional information to retrieve this value.
Using Territory Feedback
Users can query the following territory feedback data from Vault CRM and Align using Territory Feedback:
- Overview - query data about the territory and cycle
- Channel Goals - query data about the channel goals in the user's territory feedback
- Product Goals - query data about the product goals in the user's territory feedback
- Account Data - query data about the account list in the user's territory feedback
- Account Channel Goals - query data about the account list in the user's territory feedback
- Account Product Goals - query data about the product goals in the user's territory feedback
- Account Product Metrics - query data about the product metrics in the user's territory feedback
Using Calculate Data Elements as
The following calculate data elements are available:
- Add Fields (One for One) - add custom calculated fields for records in existing data elements
- Summarize - calculate one or more custom field values using data from existing data elements
- Filter List - filter a list of records from an existing data element
- Merge Lists - combines different data type selections in a single display element, for example a chart or table
- Sort List - sort a list of records from an existing data element by a calculated field
- Sublist - get a subset of a list of records from an existing data element
- Dropdown - get the selected value from a drop-down in the layout
- Date Picker - get the selected value from a picklist in the layout
Using Add Fields (One for One)
Users can add custom calculated fields for records in existing data elements using Add Fields. Users must populate the following fields when defining the calculated fields:
- Data Source – An existing data element. Only data elements with a list of records as output are available.
- Fields – List of fields to display, including fields from the data source and additional calculated fields. After selecting the data source, all of the output fields for the data source display, but can be removed. Select Add to define a calculation for a new field. For each calculated field, users must define the field name and specify the type of calculation using expressions and a list of records from any existing data element.
A one for one calculation returns a list of records. Each record can contain one or more fields.
Using Summarize
Users can calculate one or more custom field values using data from existing data elements using Summarize.
For each calculated field, users must define the field name and specify the type of calculation using expressions and a list of records from an existing data element. Select Add to add a field.
A summarize calculation returns a single record with one or more fields as output.
Using Filter List
Users can filter a list of records from an existing data element using Filter List. Users must populate the following information:
- Data Source – An existing data element. Only data elements with a list of records as output are available.
- Filter by – A boolean expression. The results only contain records for which this boolean expression is true.
Using Merge Lists
Content creators can use Merge Lists to easily combine different types of data in a single display element, for example a chart or table, by merging multiple data elements. The content creator can choose which fields in the input elements are mapped to which fields in the output. Each input maps to exactly one output field.
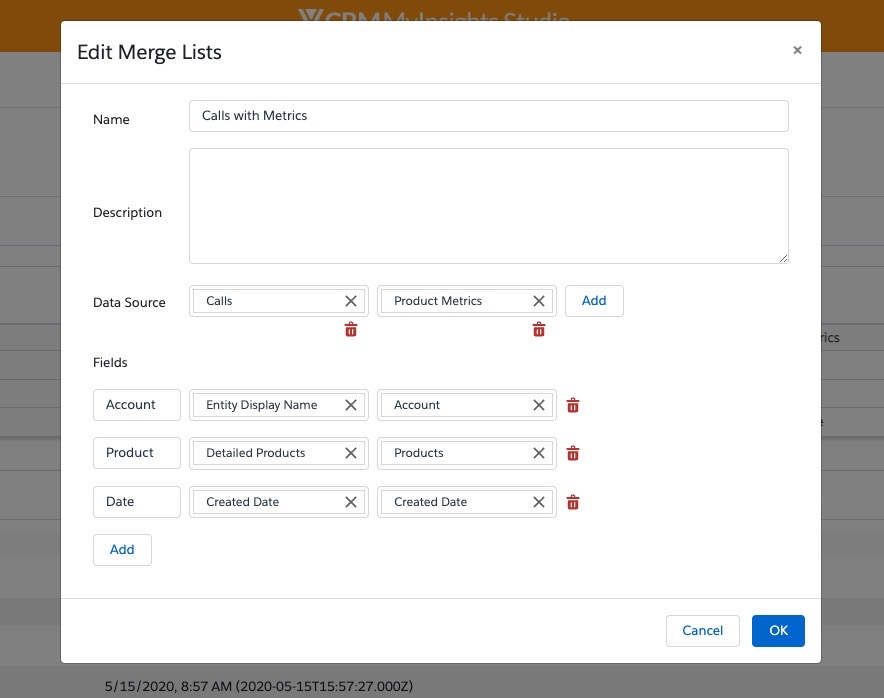
For example, users can see sales data and interaction data on the same trend chart, or recent Medical Inquiries and Medical Insights in the same table.
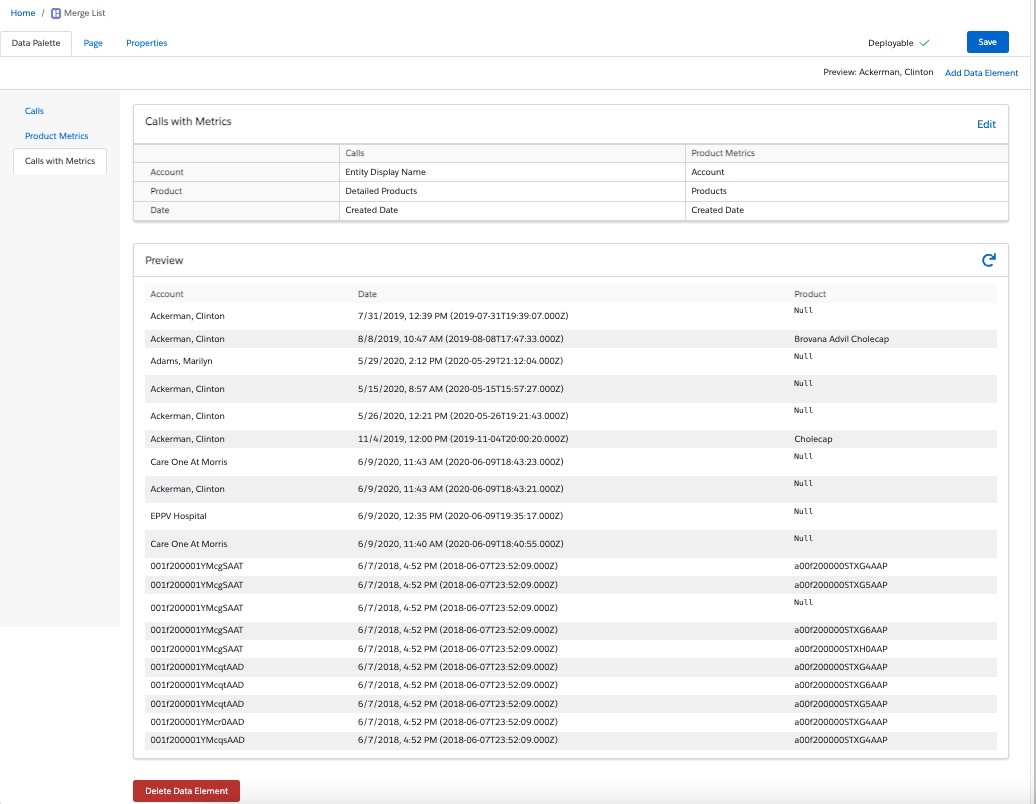
When using Deep Linking in a combined table, each table line contains a deep link to the correct object.
When configuring a View Record navigation action, X-Pages Studio automatically detects the correct object to link to based on where the ID field came from.
Using Sort List
Users can sort a list of records from an existing data element by a calculated field using Sort List. A calculated field refers to any field created as a result of a data element, for example, the One for One element. Users must populate the following information:
- Data Source – An existing data element. Only data elements with a list of records as output are available.
- Sort By – A calculated field selected from the Data Source or a data calculation entered directly. Users can select Add to add fields, which are used to sort records in case of ties. Users can select the sort order for each field.
Using Sublist
Users can get a subset of a list of records from an existing data element using Sublist. Users must populate the following information:
- Data Source – An existing data element. Only data elements with a list of records as output are available. The order of the output records is maintained.
- Skip this many – Number of records to skip, starting from the first record in the list
- Keep this many – Number of records to keep, starting from the record immediately following the last skipped record